極區(qū)是地球開向太空的天然窗口,太陽風(fēng)攜帶大量的物質(zhì)、動(dòng)量和能量沿磁力線進(jìn)入地球高層大氣,在極區(qū)電離層產(chǎn)生了大尺度的能量注入。在磁層-電離層-熱層耦合系統(tǒng)中,能量注入以焦耳熱、粒子熱和存儲(chǔ)在環(huán)電流中的能量的形式沉淀下來
[1]。電磁能是高緯電離層/熱層來自磁層和太陽風(fēng)的非常重要的能量來源。電磁能的注入則以焦耳熱的形式耗散在極區(qū)高層大氣中
[2]。高層大氣是中性大氣成分和等離子體共存區(qū)域。電磁能的注入將使得中性大氣加熱膨脹,從而改變不同高度中性大氣的密度,以及通過電離層等離子體與中性大氣成分的相互碰撞,改變電離層等離子體的溫度和密度。
基于Dynamics Explorer 2(DE-2)觀測(cè)數(shù)據(jù),Sugiura推導(dǎo)出在衛(wèi)星高度以下,由電磁能轉(zhuǎn)換的焦耳熱與Poynting通量的大小相等
[3]。利用Poynting通量方法,Olsson等人基于Astrid-2衛(wèi)星數(shù)據(jù)詳細(xì)評(píng)估了極區(qū)電離層的焦耳熱
[4]。Poynting通量分為兩種,一種是大尺度的直流Poynting通量,另一種是小尺度的交流Poynting通量,也稱為阿爾芬波Poynting通量。直流Poynting通量主要對(duì)應(yīng)著電離層的焦耳熱
[5]。沿磁力線方向(場(chǎng)向)進(jìn)入或流出電離層/熱層的電磁能,則以場(chǎng)向的直流Poynting通量表示。
極區(qū)電離層直流場(chǎng)向Poynting通量一般采用低高度極軌衛(wèi)星的觀測(cè)數(shù)據(jù)計(jì)算而來
[6-14]。美國**氣象衛(wèi)星計(jì)劃(Defense Meteorological Satellite Program, DMSP)被廣泛應(yīng)用于極區(qū)頂部電離層等離子體和磁場(chǎng)的觀測(cè)。DMSP衛(wèi)星在近圓形太陽同步軌道上運(yùn)行,軌道高度約為850 km,軌道傾角約為96°,軌道周期約為101分鐘
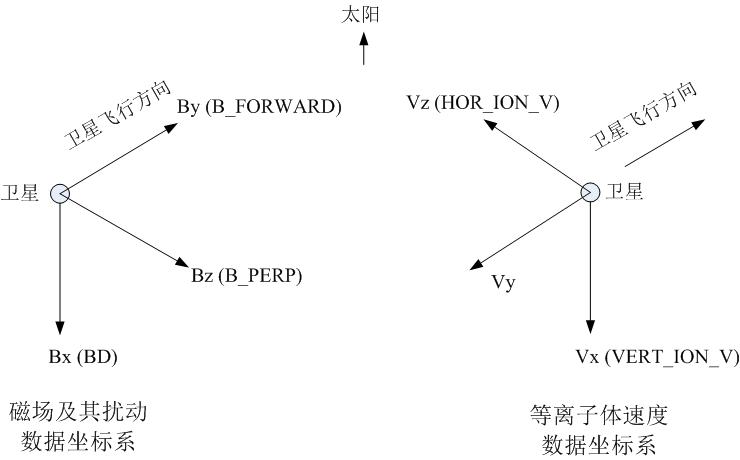
[15-18]。每個(gè)衛(wèi)星都搭載著探測(cè)電離層電子、離子密度,溫度和速度的熱等離子體探測(cè)儀(Special Sensor for Ions Electrons and Scintillations, SSIES),以及探測(cè)地球磁場(chǎng)擾動(dòng)的磁力計(jì)(Special Sensor for Magnetic Fields, SSM),還有測(cè)量沉降電子和離子的儀器(Precipitating Electron and Ion Detectors, SSJ)。目前正常運(yùn)行的有F15、F16、F17、F18衛(wèi)星。熱等離子體探測(cè)儀SSIES可提供等離子體速度(V)數(shù)據(jù)
[19],三軸磁通門磁力計(jì)SSM可提供磁場(chǎng)(B)數(shù)據(jù)
[20],從而可計(jì)算出電離層的對(duì)流電場(chǎng)E(E=-V×B)。通過衛(wèi)星測(cè)量的地磁場(chǎng)與國際參考地磁場(chǎng)(International Geomagnetic Reference Field, IGRF)作差,可以推導(dǎo)出衛(wèi)星所在位置的地磁場(chǎng)擾動(dòng)(
\(\mathrm{\delta }\mathrm{B}\))。由電離層的對(duì)流電場(chǎng)和磁場(chǎng)擾動(dòng)數(shù)據(jù),通過Poynting通量S(
\(S=\mathrm{E}×\mathrm{\delta }\mathrm{B}/{\mathrm{\mu }}_{\mathrm{o}}\)),估算出場(chǎng)向電磁能分布。
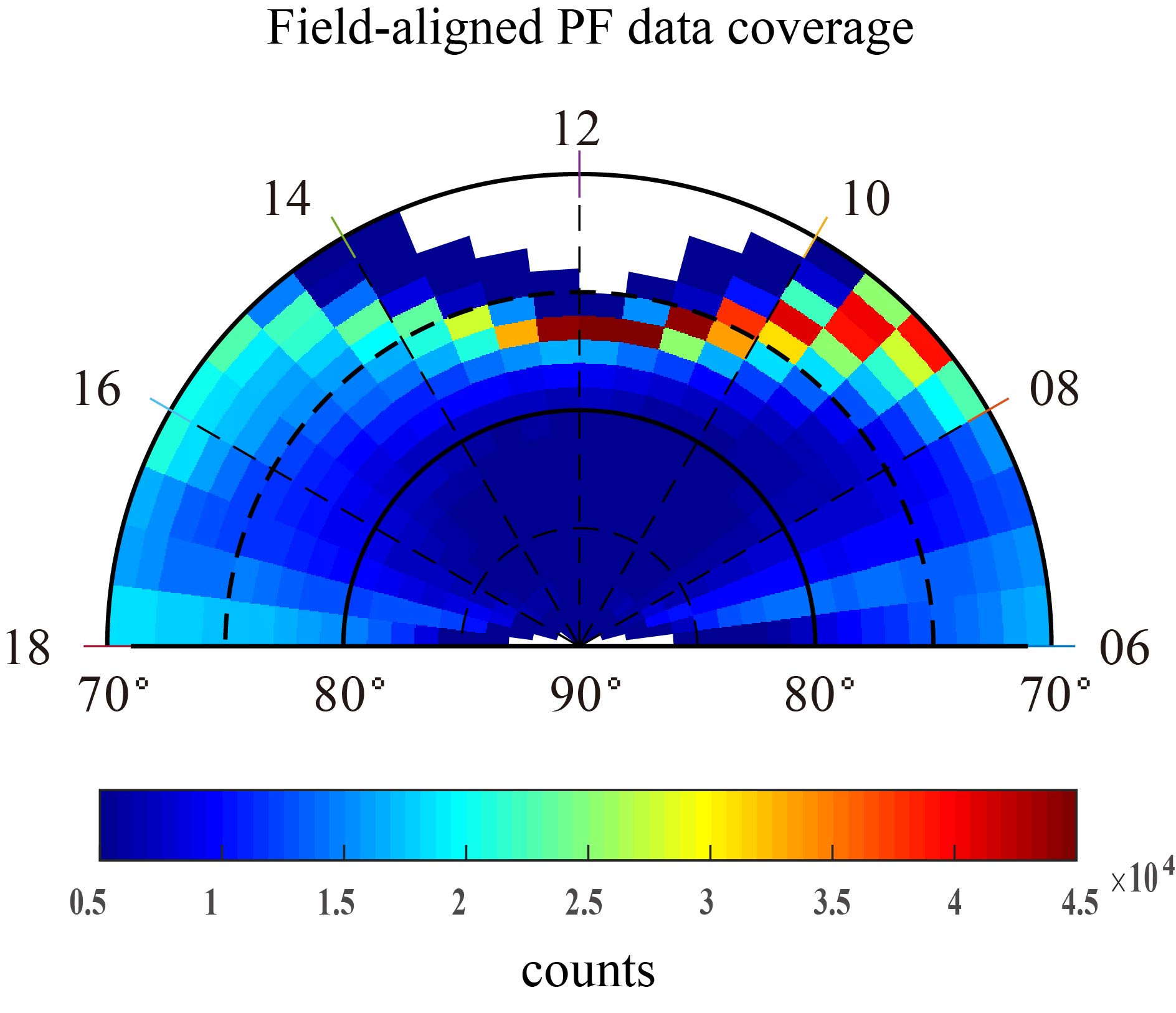
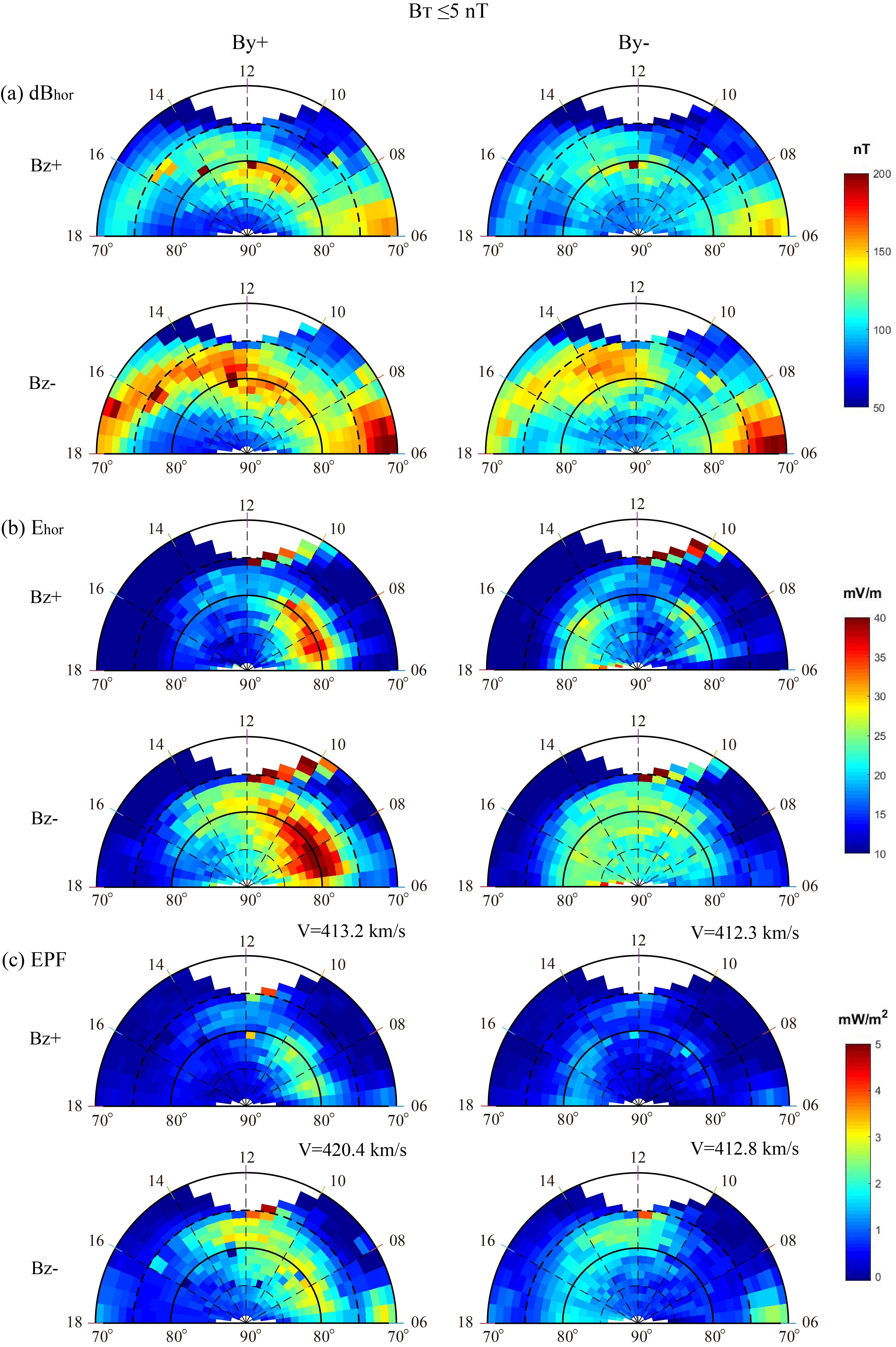
通過DMSP F17衛(wèi)星對(duì)日側(cè)頂部電離層的等離子體速度和磁場(chǎng)的觀測(cè),我們獲得約850 km高度上的水平對(duì)流電場(chǎng)、水平磁場(chǎng)擾動(dòng)和Poynting通量分布。利用這些數(shù)據(jù),我們已經(jīng)得到了頂部電離層的水平對(duì)流電場(chǎng)、水平磁場(chǎng)擾動(dòng)和電磁能的空間變化特征以及它們之間的相互關(guān)系,并且發(fā)現(xiàn)頂部電離層的電磁能分布具有晨昏不對(duì)稱性特征,而且這種不對(duì)稱性主要與水平對(duì)流電場(chǎng)分布相關(guān),此外,這些分布數(shù)據(jù)為極區(qū)電離層的電磁能傳輸和耗散研究打開了一扇新的大門,也可利用這些數(shù)據(jù)研究電磁能隨地磁活動(dòng)和行星際磁場(chǎng)的變化規(guī)律,以及電磁能對(duì)中性大氣和等離子體的加熱效應(yīng)。
基于2014–2016年北半球極蓋區(qū)的DMSP F17觀測(cè)數(shù)據(jù),本數(shù)據(jù)集提供了不同行星際磁場(chǎng)和地磁擾動(dòng)條件下日側(cè)極蓋區(qū)的場(chǎng)向Poynting通量,水平對(duì)流電場(chǎng)和水平磁場(chǎng)擾動(dòng)等數(shù)據(jù),這些數(shù)據(jù)將為極區(qū)電離層/熱層的電磁能或焦耳熱研究提供一定的數(shù)據(jù)保障。